Green Mountain Energy® Blog
Solar and Wind Energy–What’s the Difference?
Today, there is a range of different renewable energy sources, but two of the most well-known are wind and solar. Do you know the differences between the two?
Learn about the history and benefits of harnessing the power of the sun and the wind, while remembering just how impactful they both are.
Some history about wind power
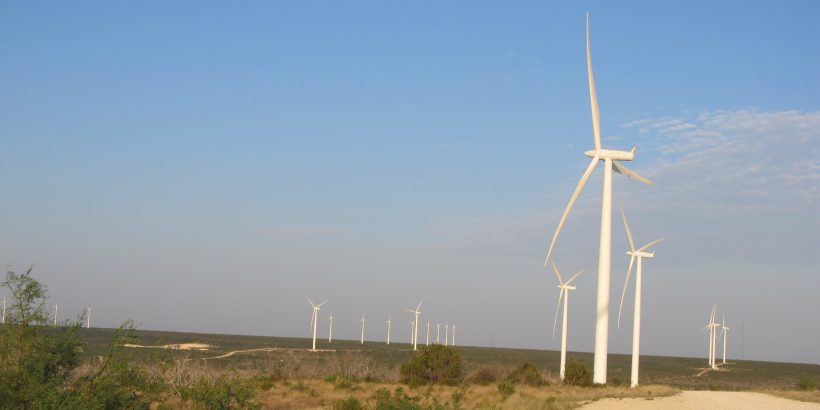
As far back as 500-900 A.D., wind power from windmills was used by the Persians for grinding grain and pumping water. The concept spread to other areas of the Middle East and eventually came to Northern Europe around 1000 A.D.
Jump ahead to 1850, and that’s when the first U.S. wind engine company was established. Thanks to the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), you can review a timeline of the history of wind power in the United States.
Pumping water for irrigation needs continued, but in 1890, the timeline notes that electricity was generated by windmills, too. A 1.25-megawatt turbine fed power to a local utility in Vermont in the 1940s.
It wasn’t until the 1970s that more research and attention was focused on the power of wind. And by the 1980s, we saw the development of the first large-scale wind farm (in California) and an ability to gauge the efficiency of turbine output.
During the 2000s, installed capacity grew from 25 to 74 gigawatts, along with the first grid-connected offshore wind turbine. The U.S. Department of Energy also published a report outlining how the U.S. could achieve generating 20% of the nation’s electricity demand using wind energy.
Get a snapshot of the history of wind power, along with a simple illustration of how a wind turbine works, by watching the video Renewable Energy 101: Wind Power.
Benefits of wind power
Pursuing the power of the wind is smart when it comes to environmental benefits, but there are also economic advantages, too. Wind power is:
- Clean
- Sustainable
- Local
- Inexhaustible
- Creating jobs in the renewable energy sector
- Considered a stable fuel cost
- Able to operate with low costs
- Easily integrated into existing landscapes
Did you know?
- The largest wind turbine in the world is located in Hawaii. It’s 20 stories tall.
- Wind power does not require any water, which helps in water conservation efforts.
- A single megawatt of wind power is enough to power 250 homes.
- More than three quarters of states produce wind energy on a large scale.
Power your home with wind
You don’t have to erect a windmill or wind turbine in your backyard to power your home with clean wind energy. You can use wind power for all your electricity needs with our clean electricity plans. Simply use your zip ZIP code to find a 100% wind energy plan that works for your household’s needs.
Now that you’re equipped with some wind knowledge, let’s look at the other well-known renewable energy source, the sun.
Some history about solar power
Thanks again to the EERE, you can review a timeline of the evolution of solar power, from the 7th century B.C. to 2002.
In the earliest days, magnifying glasses and burning mirrors were used to light torches for religious purposes and make fire. And positioning structures and dwellings to utilize the warmth of the sun was common among the Romans and the Anasazi (ancestors of the Pueblo people).
It was in 1767 that Swiss scientist Horace de Saussure built the first solar collector. And in 1839, French scientist Edmond Becquerel discovered that electricity generation increased when exposed to light (the photovoltaic effect).
In the 1800s and 1900s, many contributed to the advancement of solar power, including Samuel P. Langley (developed the bolometer, which measured light); Albert Einstein (produced a paper on the photoelectric effect); and Jan Czochralski (grew single-crystal silicon).
It was in 1954 that Bell Labs developed the first solar cell capable of converting solar energy into power for electrical equipment. Some of the earliest solar-powered devices were the dollar bill changer and a decoder for computer punch cards and tape.
In 1964, NASA powered one of its satellites with a 470-watt photovoltaic array. And the U.S. Department of Energy created a laboratory dedicated to solar energy research in 1977.
Advancement continued in the 1980s and 1990s with solar cells, photovoltaic modules and systems, concentrating solar power technology, conversion efficiency, distributed power (the first grid-supported system was in California), solar panels and storage techniques.
The year 2001 is when Home Depot began selling residential solar power systems and when the largest rooftop solar power system was installed in the U.S. (a 1.18-megawatt system in California).
Governmental regulations and incentives, public policies, cost, accessibility, manufacturing, materials and many other factors will determine just how bright the future is for solar. But looking at its history, the outlook appears to be sparked with powerful potential.
The video Renewable Energy 101: Solar Power is less than two minutes and offers a look at the power of the sun, including an explanation of how solar panels work.
Benefiting from solar power
Solar energy, like wind, has many environmental and economic benefits. Solar power is:
- Clean
- Inexhaustible
- Sustainable
- A way to increase your home’s value (with your own solar panels)
- Helpful in reducing electricity bills (when producing your own power)
- Able to operate with low maintenance costs
- Versatile (generate electricity with photovoltaics or heat using solar thermal)
- Efficient, since excess generated electricity can be sent to the grid
Did you know?
- The sun is the most abundant energy source in our solar system.
- Solar power is used to create electricity, heat water, cook food and power vehicles.
- The earth gets more energy from the sun in one day than the whole world’s population uses in an entire year.
- Solar power is used on a wide scale, but it only provides a fraction of the world’s energy supply.
Power your home by the sun
You have options to go solar for your energy needs.
You can take full control by installing solar panels on your rooftop. You’ll save money on your monthly utility bill and shrink your carbon footprint, preventing more than 17,000 pounds of CO2 emissions a year!
As a clean energy leader, we’ve got you covered to make the solar step. We’re equipped with a one-stop shop to guide you on preferred installation partners, along with an installation rebate to save you thousands on installation costs.
Take the time to see if you’re ready to go solar.
If you aren’t ready for solar at your home, but you want to help the solar power movement, sign up for SolarSPARC® (Smart People Accelerating Renewable Change).
SolarSPARC® accelerates the growth, adoption and innovation of solar energy. Look at the projects and programs it’s funded already.
You’ll benefit by becoming a SolarSPARC® customer:
- Use a solar power plan for your home.
- Feel empowered by helping to fund solar-related technologies and programs that help make solar more affordable for all.
Knowing that clean, renewable energy, like wind and solar power, makes such a positive impact on the planet means now you just need to decide how to do your part. Do you power your home with a 100% pollution-free electricity plan, using wind or solar, or do you install your own solar array?
Either way, we have you covered and are ready to help. Get started on the path to renewable energy and be part of wind and solar power history.
Find a renewable energy plan that helps your business go green.
Enter your ZIP code to get started.
Blog Categories
Related Articles
Our customers have avoided
pounds of CO2
That’s like planting
new trees.