What Is Biomass Energy?


What Is Biomass Energy?
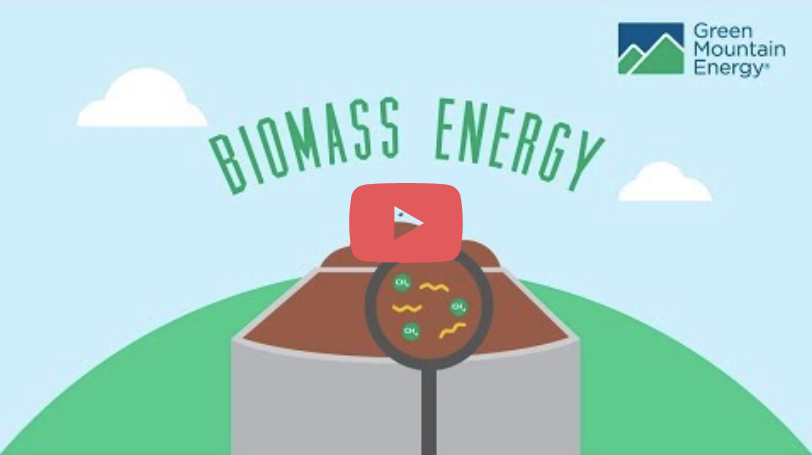
How biomass energy works:
While there are many sources of biomass energy, there are two major ways to harness biomass energy to generate electricity: burning and decomposition.
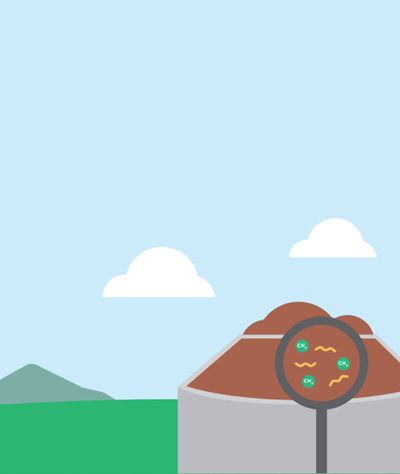
1 Depending on what type of biomass is used, the organic waste is either burned to produce heat or decomposed to produce methane gas, which is then burned to produce heat.
2 Heat – biomass energy – is used to boil water, which turns into steam.
3 The steam spins a turbine which then powers a generator and creates the electricity we can use to power our lives.
Types of biomass energy:
If left to decompose on its own, landfill and animal waste will release its methane into the atmosphere. Since methane is a potent greenhouse gas with 25 times the heat-trapping ability of carbon dioxide, it’s the second-biggest contributor to climate change when it escapes into the atmosphere. If we can capture methane for use as a biomass energy source, we can help reduce the effects of climate change in two ways!
Biomass facts:
Choose a clean energy plan with Green Mountain Energy.
Biomass energy is just one of the ways that we can put waste products to good use and reduce our carbon footprint. When you choose to power your home with 100% renewable energy, you can do your part to make sure that the future looks cleaner and greener.
Join our mission to inspire hope and motivate action
through the use of clean energy. Sign up for a 100%
renewable energy plan and help build a cleaner, greener
tomorrow for everyone.
Explore more renewable energy sources:
*U.S. Energy Information Administration
This page is for general educational purposes only.
Our customers have avoided
pounds of CO2
That’s like planting
new trees.