-
Hydropower is one of the least expensive renewable energy sources in the United States.

What Is Hydroelectricity?


What Is Hydroelectricity?
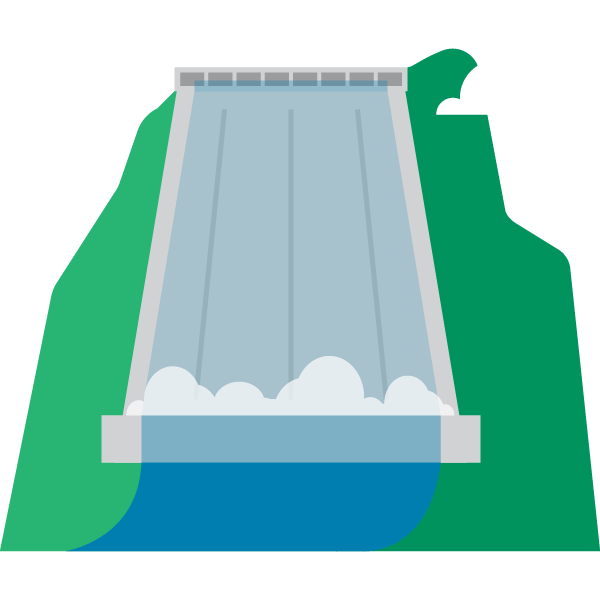
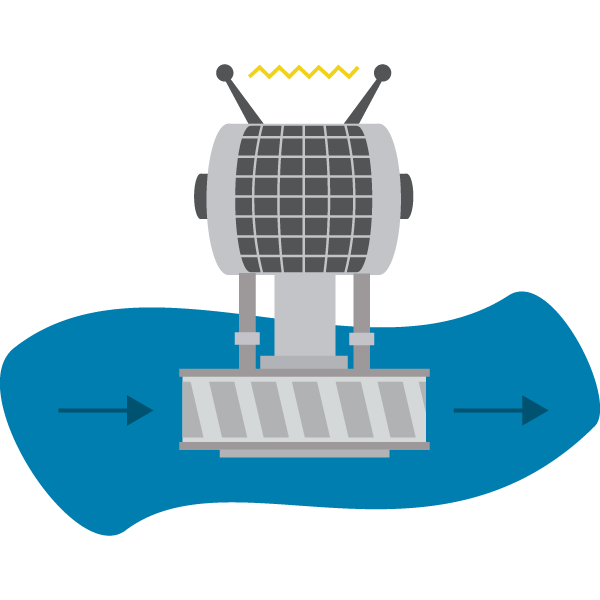
How hydroelectricity works:
Despite the countless technological advancements we’ve made since we started using hydropower, the principles of harnessing hydroelectric energy are much the same as they were thousands of years ago.
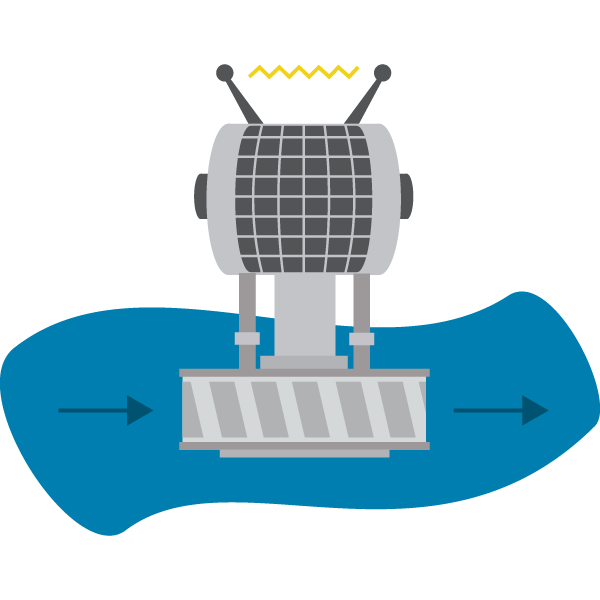
Types of hydropower energy plants:
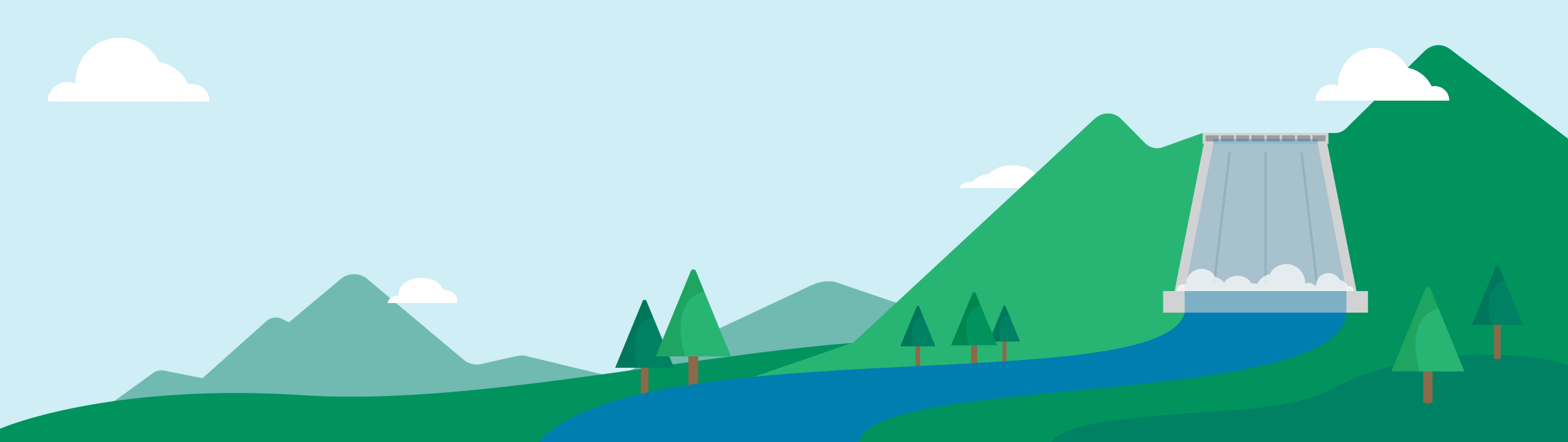
There are three major types of hydroelectric power plants that are used to generate electricity. Each type uses a different method for moving a turbine and generating electricity for the grid to use.
Advantages of hydropower — and some challenges.
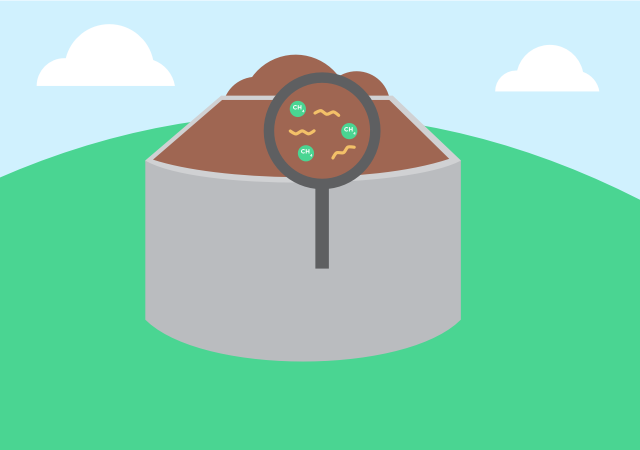
Hydropower is one of the oldest energy sources in human history. And though we harness it for a different purpose in the modern day, there are still things we need to consider when deciding to use hydroelectricity.
-
Hydropower can be captured from many different forms of water, including river currents, river dams, ocean waves and ocean tides.
-
Hydropower reservoirs depend on weather trends and precipitation to stay full, impacting its reliability as droughts and other conditions related to climate change become more common.
-
Hydroelectric facilities have the potential to adversely affect their surrounding environments due to the disruptions in the natural flow of water, so they must be carefully constructed and operated.
Ready to power your life with 100% clean, renewable energy? Shop for electricity plans that are available in your area.
*U.S. Energy Information Administration
This page is for general educational purposes only.
Explore more renewable energy sources:
Our customers have avoided
pounds of CO2
That’s like planting
new trees.